Deep Learning
I
n our laboratory we are researching on artificial intelligence, especially applying Deep Learning in areas such as vision and natural language. We are quite aware that this is the future, so we decided to see what projects could solve problems of our country and the world. We are currently experimenting, replicating (sometimes improving) projects already published and also creating our own.
Reinforcement Learning
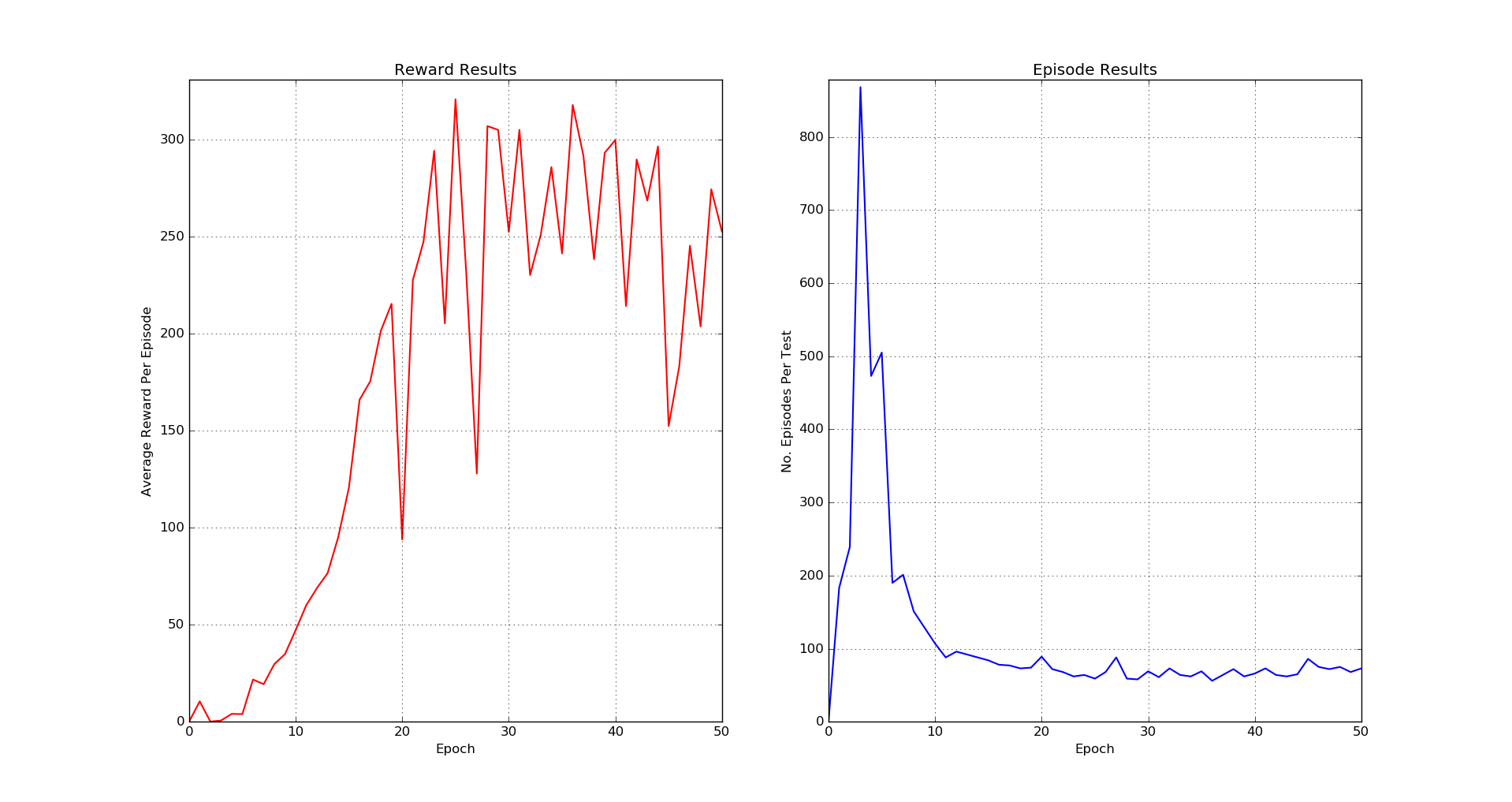
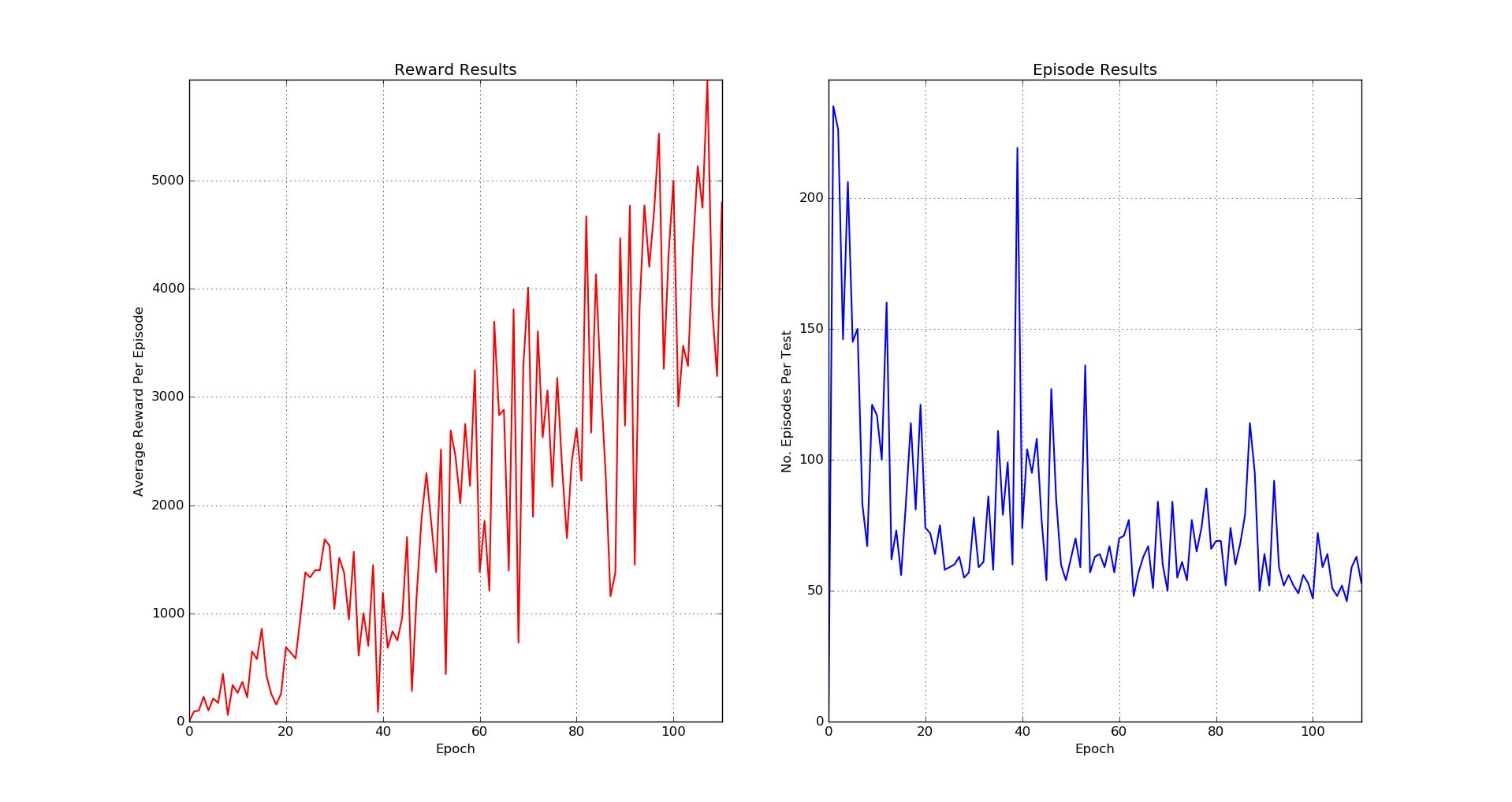
In 2015 DeepMind published a paper called Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning where an artificial intelligence through reinforced learning could play Atari games. This was shocking news, since the agent learns by simply viewing the images on the screen to perform actions that lead to a better reward. It was so successful, that in some games, it was able to surpass expert humans. We decided to recreate the results, so using python, theano, ALE (Arcade Learning Environment) and a Nvidia GPU we did it and here are our results:
Breakout - Epoch 25
Breakout - Results
Seaquest - Epoch 107
Seaquest - Results
If you want to train/test an agent, you can use our code that is in a GitHub repository that has the necessary instructions to do it: DeepQNetwork
Classification and Localization
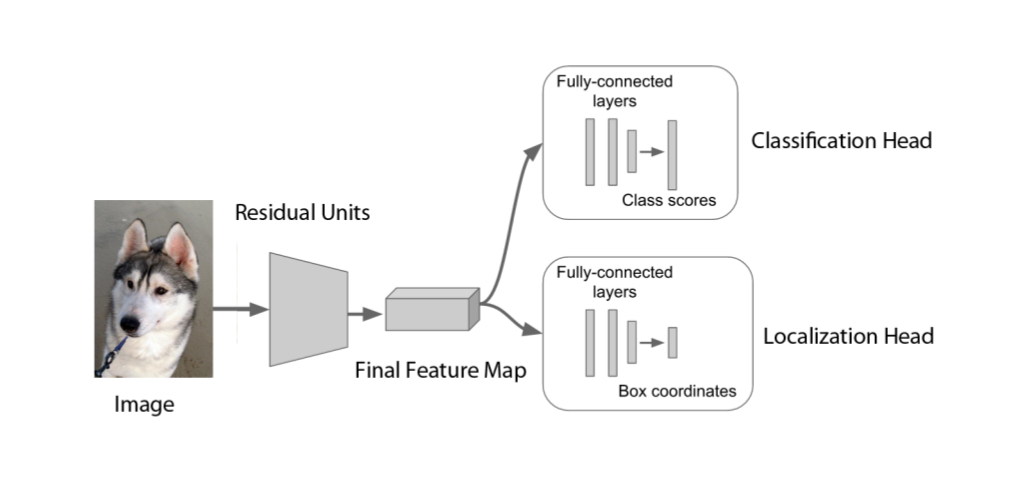
DogBreedsCL is a system able to classify dog breeds and also locates in which part of the image a dog is (surrounded by a bounding box). This project was motivated to understand the power of residual neural networks and feature extraction. We used a deep convolutional residual network of 152 layers pre-trained in the ImageNet dataset, then we removed the last classification layer to use the features of the last convolutional layer and only trained a new classification and localization layer. After all this we were able to achieve a classification accuracy of 94% in the test set of the Stanford Dogs Dataset.
Neural Net Architecture
Classification & Localization Run
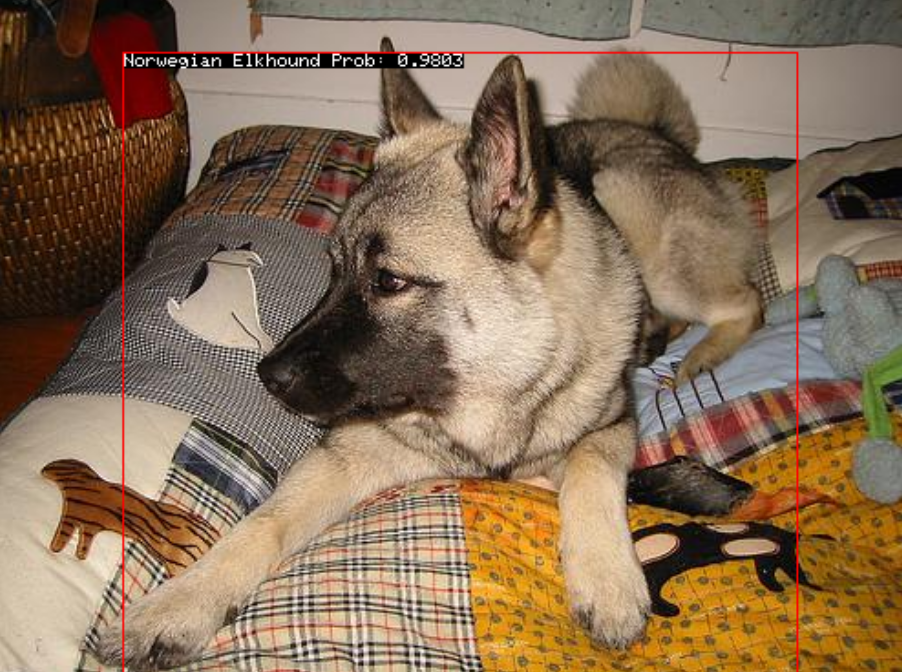

Image Captioning
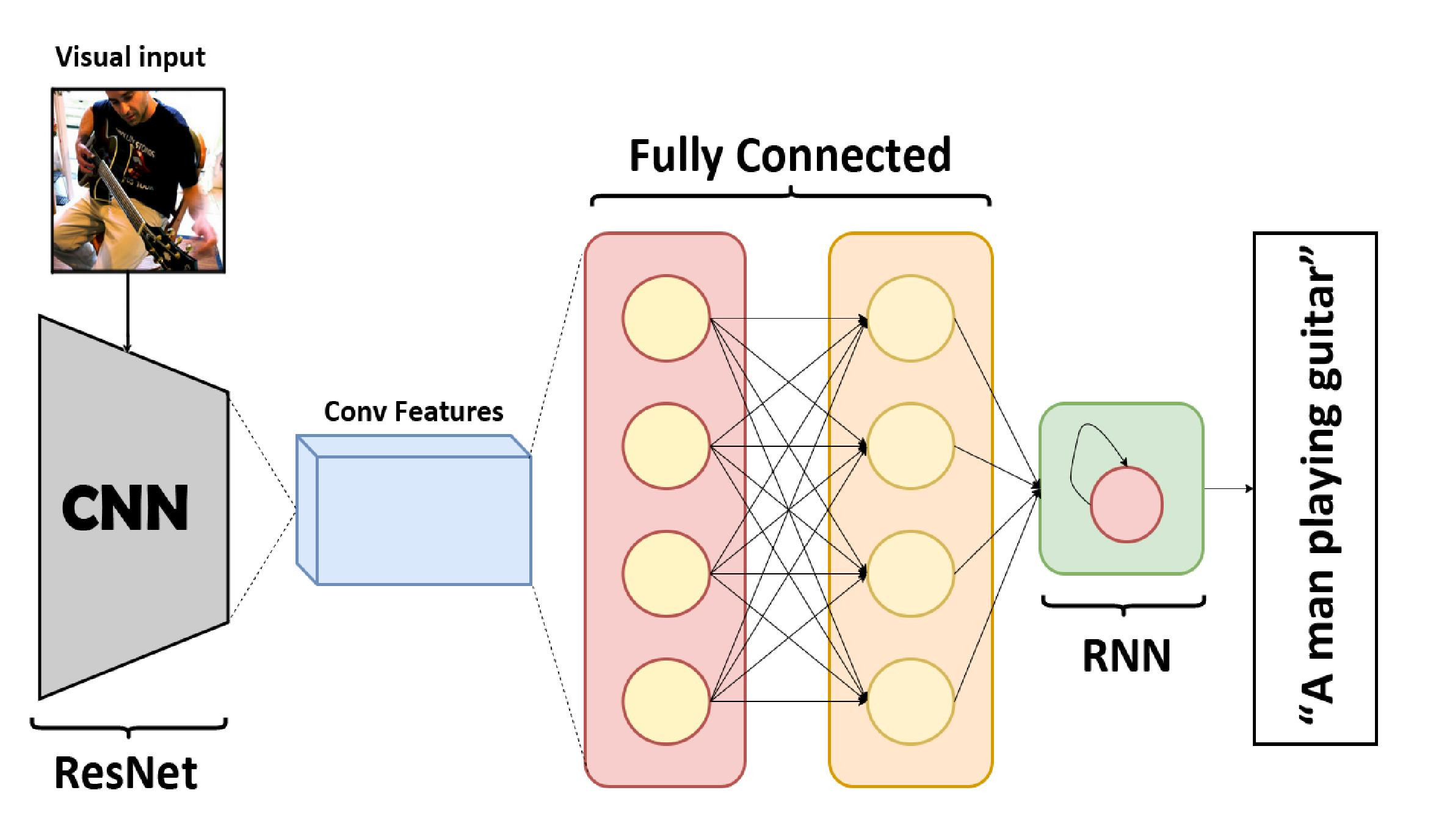
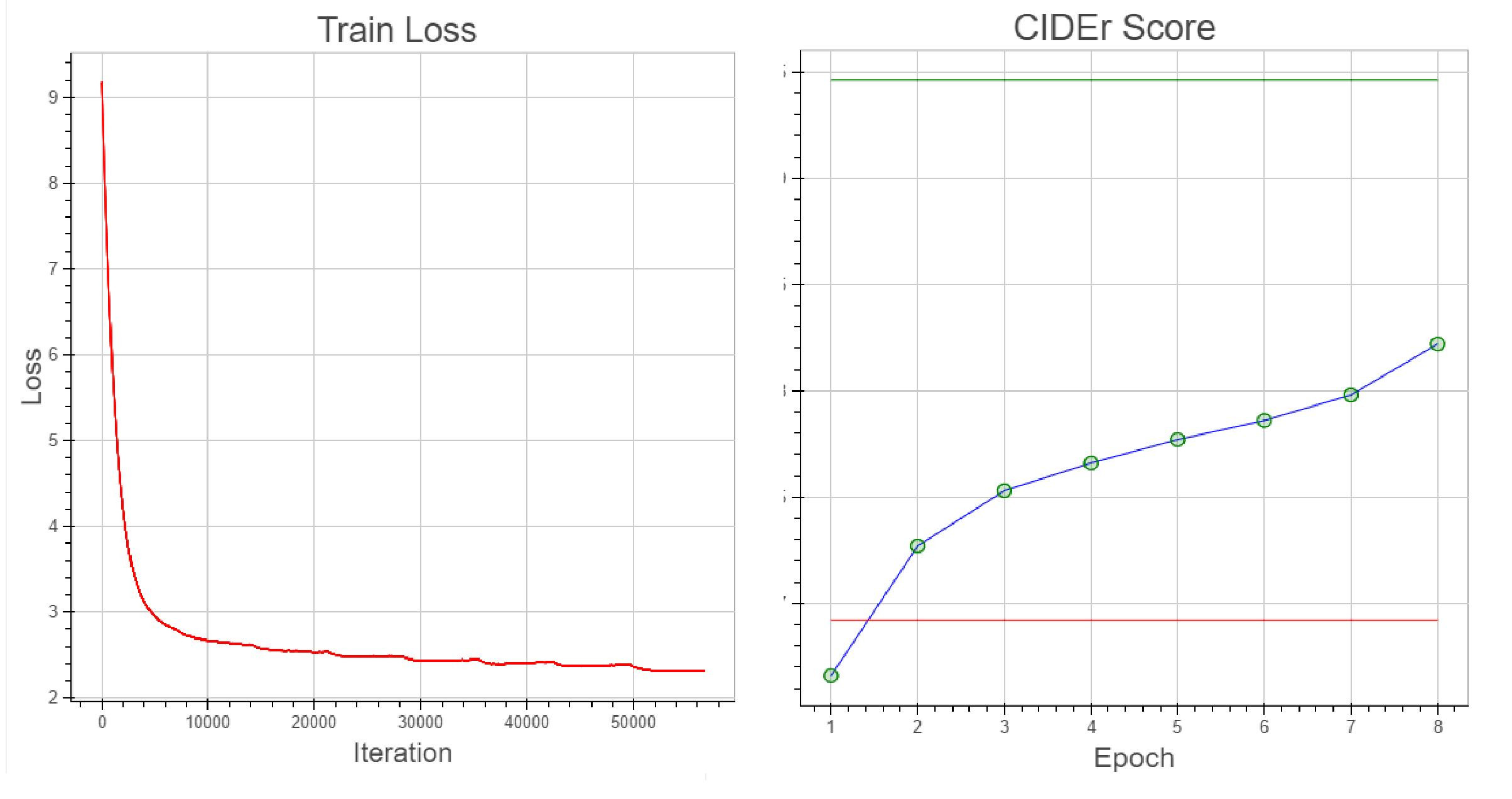
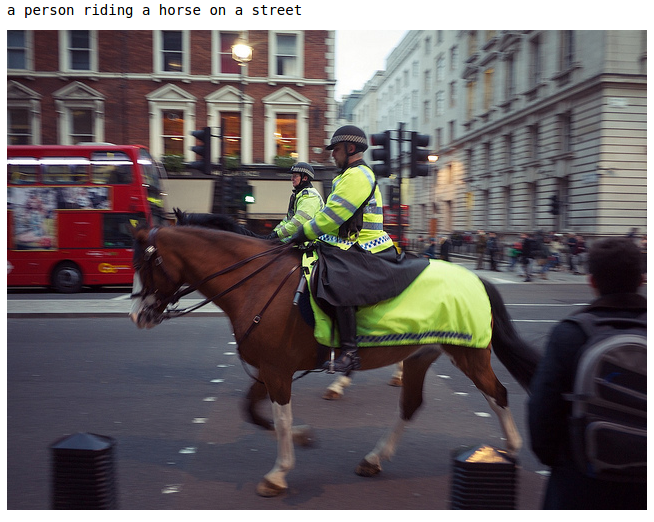
Thanks to the latest advances in natural language processing and deep learning it is possible to create systems that do quite cool tasks, like an image caption generator, where with a neural network we can generate (in the case of a generative model) a description of an image. We wanted to do this with a generative model using a residual neural network and a recurrent neural network (LSTM). We join this project with Leonardo GreenMoov Project using a text2speech program and his cameras, Leo can see and describe his surroundings. In this project our results were good, reaching a CIDEr score of 0.8 in the COCO Val Dataset.
Model Architecture
Model Results
Model Test

Self-Driving Cars
A few years ago the boom of autonomous cars began and now with more strength. Although we are not where we want, significant progress has been made. We are currently taking a course on this subject (Udacity Self-Driving Car Engineer Nanodegree) and with the knowledge acquired we have done some cool projects like: Lane Lines Detection, Traffic Sign Classifier and Behavioral Cloning.
Lane Lines Detection
When we drive, we use our eyes to decide where to go. The lines on the road that show us where the lanes are act as our constant reference for where to steer the vehicle. Naturally, one of the first things we would like to do in developing a self-driving car is to automatically detect lane lines using an algorithm. We detect lane lines in images using Python and OpenCV.
GitHub Repo
$ git clone https://github.com/andrescv/Lane-Lines-Finder.git
Traffic Sign Classifier

We used deep neural networks and convolutional neural networks to classify german traffic signs. The dataset used is the German Traffic Sign Dataset. After the model was trained, we tried out our model on images of German traffic signs that we found on the web and we obtained an accuracy of 97%.
GitHub Repo
$ git clone https://github.com/andrescv/Traffic-Sign-Classifier.git
Behavioral Cloning
In this project we used a convolutional neural network to predict the steering angle only by seeing the road through a central camera. To train the network we used the images of the central camera of the Udacity simulator and a L2 Loss
\[L(\theta) =\frac{1}{N}\sum(y_{pred} - y)^2\]GitHub Repo
$ git clone https://github.com/andrescv/BehavioralCloning.git